DAY1(STL) HDU1880魔咒词典 字符串Hash /map/)
水题,两个map即可,细节在于string用cin读还是getline读,然后可以用string的erase来去掉中括号【】
以上的话,是提交卡在队列里时自信打出来的。最后发现是水的是我。。。
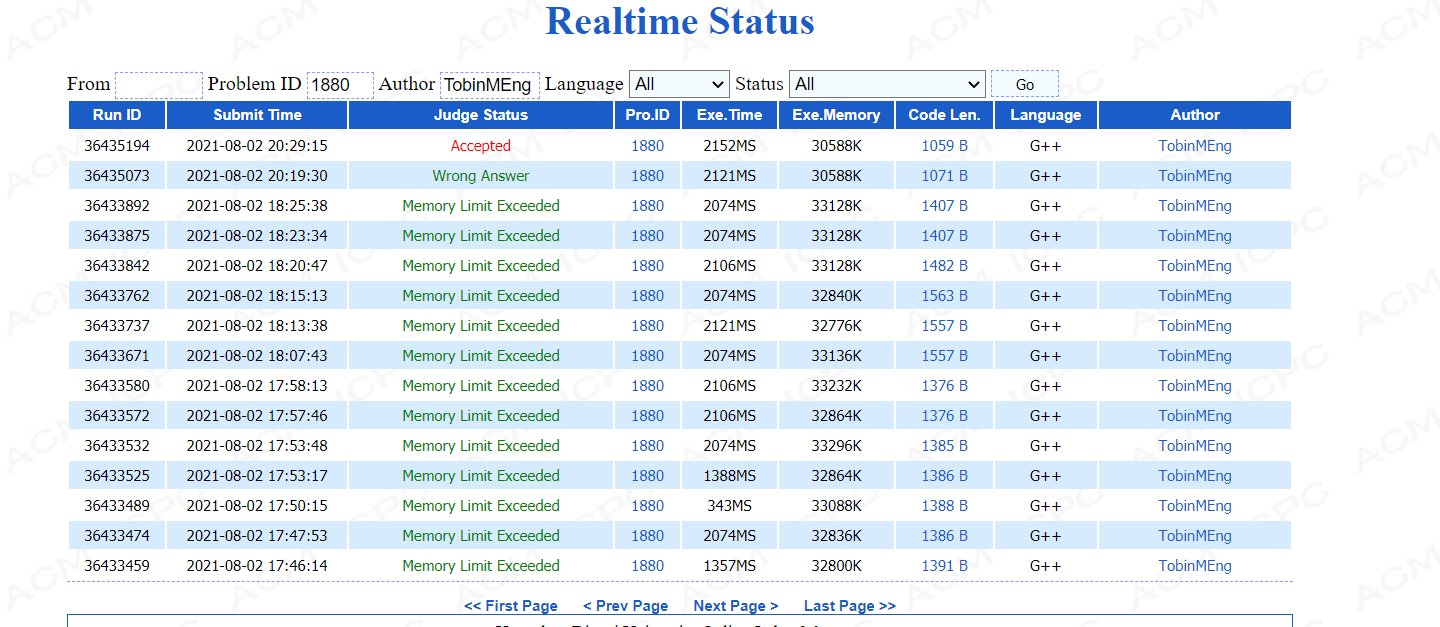
用两个map的话交一遍就会发现一定会MLE。。。而且HDU的MLE规则很奇怪,不要尝试参考评测机的内存大小来调数组的大小,没有用的。。以图为证:
是的,我MLE了20多次,都是在尝试调数组的大小。。。。。
正解应该是Hash+挂链法或者寻址法,但是我写的挂链法也还是MLE。。。最后选择了zy选择的vector。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int maxn = 100010 ;int > a, b; int cnt, n;int gethash (string s) int res = 0 , leng = s.length ();for (int i=0 ;i<leng;++i)237 + s[i];return res;int main () while (cin >> t1 && t1 != "@END@" ) {getchar ();getline (cin, t2);int c1 = gethash (t1);int c2 = gethash (t2);push_back (c1);push_back (c2);getchar ();for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) {getline (cin, t1);int tmp = gethash (t1);if (t1[0 ] == '[' ) {if (find (a.begin (), a.end (), tmp) == a.end ()) cout << "what?" << endl;else cout << s2[find (a.begin (), a.end (), tmp) - a.begin ()] << endl;else {if (find (b.begin (), b.end (), tmp) == b.end ()) cout << "what?" << endl;else {find (b.begin (), b.end (), tmp) - b.begin ()];for (int i=1 ;i<s3.length ()-1 ;++i) cout << s3[i];return 0 ;
HDU1276士兵队列训练问题 模拟 /约瑟夫环)
用vector完成,简单模拟,水题。
第一遍没有注意输出空格PE了一次,第二遍A了
代码(比较丑陋):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 #include <map> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std;int > a, b;int n, m;int vsize () int leng = a.size (), res = 0 ;for (int i=1 ;i<leng;i++) {if (a[i] != -1 ) res++;return res;void work () int flag = 0 , leng;while (vsize () > 3 ) {size ();if (!flag) {for (int i=1 ;i<leng;++i) if (i % 2 == 0 ) {-1 ;else {for (int i=1 ;i<leng;++i) if (i % 3 == 0 ) {-1 ;for (vector<int >::iterator it=a.begin ();it!=a.end ();it++) {if (*it == -1 ) {erase (it);1 ? 0 : 1 ;int main () for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) {clear ();clear ();push_back (0 );for (int j=1 ;j<=m;++j) a.push_back (j);work ();for (vector<int >::iterator it=a.begin () + 1 ;it!=a.end ();it++) {if (*it != -1 )push_back (*it);for (vector<int >::iterator it=b.begin ();it!=b.end ();it++) {if (it != b.end () - 1 ) ' ' ;else cout << *it;return 0 ;
牛客 吐泡泡 栈 )
点开之后发现5月的时候写过了。。。看了一下发现记不得自己是怎么做了,估计是要老年痴呆了(确信)
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, a, n) for (int i=a;i<=n;++i) #define per(i, n, a) for (int i=n;i>=a;--i) #define enter putchar('\n' ) typedef long long ll;using namespace std;char > sk;int len;int main () while (cin >> s) {"" ;length ();rep (i, 0 , len - 1 ) {if (sk.empty ()) {push (s[i]);continue ;else {char temp = sk.top ();if (temp == s[i]) {if (temp == 'o' ) {pop ();if (sk.size () && sk.top () == 'O' ) sk.pop ();else sk.push ('O' );else sk.pop ();else sk.push (s[i]);while (sk.size ()) {top ();pop ();per (i, ans.size () - 1 , 0 ) cout << ans[i];return 0 ;
DAY2(单调栈、单调队列、ST表) POJ - 3250Bad Hair Day
由题可知将答案求每个羊可以看到多少只右边的羊转化为求每一个羊可以被多少左边的羊看到,然后在纸上模拟一下就可以发现单调栈满足这个过程。单调栈和单调队列难都是在思路的转换,一眼会想不到。
代码(摘了眼镜看形状好奇怪啊。。):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std;typedef long long ll;int main () push (tmp);for (int i=1 ;i<n;++i) {while (st.size () && st.top () <= tmp) st.pop ();size ();push (tmp);return 0 ;
POJ - 2823 Sliding Window
如果我们要得到区间的最大值,那我们可以维护一个队列,在里面存一些我们遇到过的比较大的值,并且保证这个队列是递减的。那么如果我们这时拿到一个新的数据,我们只需要把这个数据放到当前队列的正确的位置然后取队首元素就能找到最大值了。
由于该队列是单调递增的,所以只需要将新的数据和队尾的值进行比较,如果队尾的值比较小,那么直接扔掉,因为我们要得到的是区间的最大值,所以舍去一些比较小并且比较旧的值并没有什么影响。
对于这道题最后需要注意的是处理完数据之后的队首是否在当前数据的窗口中,若不在,那么将旧数据直接舍弃即可。
处理区间的最小值同理。
对于队列维护的模拟可以看这个博客 。
这道题还有一些小坑。因为在POJ上,会比较慢,用deque会T掉,可以用数组模拟一个双端队列。然后常数大也会被卡掉,所以要用快读。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <deque> using namespace std;const int maxn = 1e6 +7 ;int n, k;int a[maxn], b1[maxn], b2[maxn], tot1, tot2, h1, h2, t1, t2;int , int > q1[maxn], q2[maxn];inline int read () int a=0 ,f=1 ; char c=getchar ();while (c<'0' ||c>'9' ) {if (c=='-' ) f=-1 ; c=getchar ();}while (c>='0' &&c<='9' ) {a=a*10 +c-'0' ; c=getchar ();}return a*f;void init () sync_with_stdio (false );read ();k=read ();for (int i=1 ;i<=n;++i) a[i] = read ();1 , h2 = 1 , t1 = 1 , t2 = 1 ;inline void write (int x) if (x>9 )write (x/10 );putchar (x%10 +'0' );void solve () for (int i=1 ;i<k;++i) {while (h1 < t1 && q1[t1-1 ].first <= a[i]) t1--;while (h2 < t2 && q2[t2-1 ].first >= a[i]) t2--;for (int i=k;i<=n;++i) {while (h1 < t1 && q1[h1].second <= i - k) h1++;while (h2 < t2 && q2[h2].second <= i - k) h2++;while (h1 < t1 && q1[t1-1 ].first <= a[i]) t1--;while (h2 < t2 && q2[t2-1 ].first >= a[i]) t2--;void print () for (int i=1 ;i<=tot1;++i) if (i!=tot1) printf ("%d " ,b2[i]); else printf ("%d\n" ,b2[i]);for (int i=1 ;i<=tot2;++i) if (i!=tot2) printf ("%d " ,b1[i]); else printf ("%d" ,b1[i]);int main () init ();solve ();print ();return 0 ;
POJ - 3264 Balanced Lineup ST表 /线段树/树状数组)
这道题是学长讲的ST表的例题,本质是一个RMQ。
ST表,是利用倍增和动态规划的思想处理出的一个查询表,需要用nlogn的时间预处理,得到ST表之后,就可用O(1)的时间查询任意区间内的极值。
ST表的预处理的状态转移方程:d1[i][j]=min(d1[i-1][j],d1[i-1][j+bin[i-1]]); i表示2的i次方,j表示某个点。对于每一个点的所有有意义的2的i次方长度的区间内的极值都需要求出。
ST算法进行查询的核心是在预处理出每个端点本身开始往后的2的i次方的范围内的每一个2区间内的极值后。对于每一次查询,找到满足区间长度r - l + 1所能满足的最大的2的x次方,然后将长度分为两半,以2的x-1次方为区间长度对两个端点的左右进行查询,O(1)的复杂度,然后取这两个值中的极值即为区间的极值。
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Keep_Trying_Go/article/details/116268533 https://blog.csdn.net/Hanks_o/article/details/77547380
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <cstring> #define rep(i,a,b) for (int i=a;i<=b;++i) using namespace std;const int maxn = 50010 ;int n, q; int a[maxn], bin[30 ], Log[maxn];int d1[30 ][maxn], d2[30 ][maxn];void init () memset (a,0 ,sizeof memset (d1,0 ,sizeof memset (d2,0 ,sizeof 0 ] = 1 ;Log[0 ] = -1 ;rep (i,1 ,n) cin >> a[i];rep (i,1 ,20 ) bin[i] = bin[i - 1 ] * 2 ;rep (i,1 ,50001 ) Log[i] = Log[i/2 ] + 1 ;rep (i,1 ,n) d1[0 ][i] = d2[0 ][i] = a[i];rep (i,1 ,Log[n]) {rep (j,1 ,n) {if (j+bin[i]-1 <=n) { min (d1[i-1 ][j],d1[i-1 ][j+bin[i-1 ]]);max (d2[i-1 ][j],d2[i-1 ][j+bin[i-1 ]]);void query (int x ,int y) int t = Log[y-x+1 ];int a = max (d2[t][x],d2[t][y-bin[t]+1 ]);int b = min (d1[t][x],d1[t][y-bin[t]+1 ]);int main () init ();rep (i,1 ,q) {int a, b;query (a, b);return 0 ;
POJ - 2559 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
单调栈的应用。
对于每一个长方形来说,如果不重复计算的话,这道题的答案就是每个长方形向右画的长方形中面积最大的那一个。
接着想,对于某个长方形,它所能画出的最大高度就是他本身,最大宽度就是他往右的连续的不低于他的长方形的宽度。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #define rep(i,a,b) for (int i=a;i<=b;++i) using namespace std;typedef long long ll;const int maxn = 100010 ;inline void init () memset (w, 0 , sizeof memset (a, 0 , sizeof memset (s, 0 , sizeof 0 , tail = 0 ;1 ] = 0 ;rep (i,1 ,n) cin >> a[i];void solve () rep (i,1 ,n+1 ) {if (a[i] > s[tail]) {1 ;else {int width = 0 ;while (a[i] < s[tail]) {max (ans, (ll)width * s[tail]);1 ;int main () while (cin >> n && n != 0 ) {init ();solve (); return 0 ;